Topic: React Basics
My React Learning Note (1)
Topic: React Basics
State V.S Props
Every time a state is changed, the JSX gets rendered again
One direction data flow: State=>Props
Therefore, Every time when a state changes, all the props of that state is rendered again!
Synthetic Event
Event Handler that will only be triggered when a specific event happens.
Error function
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 this .handleChange = this .handleChange.bind(this );handleChange (e )this .setState({ searchField : e.target.value });
this is equivalent to
1 2 3 4 (e ) => {this .setState({ searchField : e.target.value });
React and ReactDOM
1 2 3 4 5 6 <script>const App = () => {return React.createElement("div" , {}, React.createElement("h1" , {}, "React Is Rendered!" )document .getElementById("root" ))
React Package Update
1 2 3 npm updatenpm list react react-dom react-scriptsnpm audit fix
Virtual DOM / Unidirectional Data Flow
1 Actual Dom ------->
Virtual Dom is a copy of Actual Dom:
Every time a component is re-rendered, a Virtual Dom is copied
Compare with the Actual Dom, see what is different(re-rendered)
Make update in Actual Dom
Unidirectional Data Flow:
Data only affects the children of nodes! Therefore, state should be placed wisely so that minimal number of nodes shall be updated
Async setState
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 () => {this .setState({ coins : this .state.coins+1 })() => {this .setState((prevState, prevProps ) => {return {cois : prevState.coins+1 } ()=> console .log(this .state.coins) )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class App extends React .Component constructor (props )super (props);this .props = props
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class App extends React .Component 47
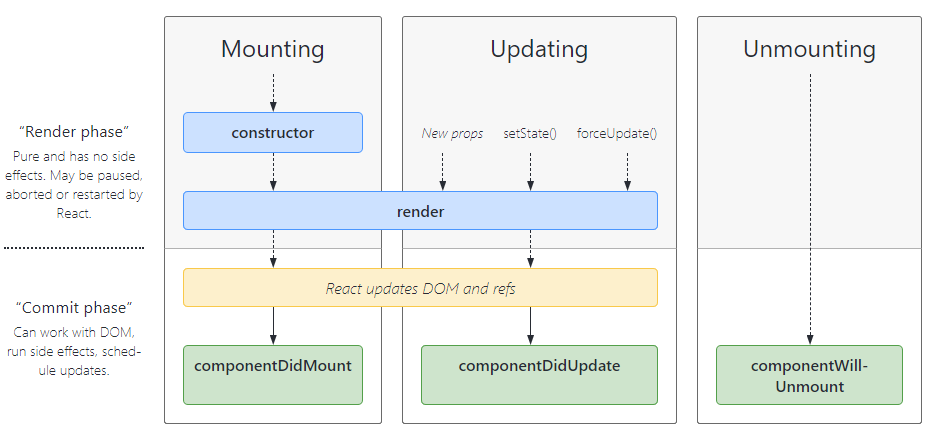
Life Cycle Methods of Class Component
1 {this .state.showChild}? <Lifecycles text ={this.state.text} /> null
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Lifecycles extends React .Component constructor (super ();console .log("constructor!" )componentDidMount (console .log("componentDidMount!" )componentDidUpdate (console .log("conponentDidUpdate!" )componentWillUnmount (console .log("componentWillUnmount!" )shouldComponentUpdate (nextProps, nextState )console .log("shouldComponentUpdate!" )return nextProps.text !== this .props.textrender (console .log("render!" )return ('lifecycles' >this .props.text}
React lifecycle methods diagram